Your cart is currently empty!
2 2 Future Value of Annuities Mathematics of Finance
The present value of annuity calculator is a handy tool that helps you to find the value of a series of equal future cash flows over a given time. In other words, with this annuity calculator, you can compute the present value of a series of periodic payments to be received at some point in the future. The discount rate reflects the time value of money, which means that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future because it can be invested and potentially earn a return. The higher the discount rate, the lower the present value of the annuity, because the future payments are discounted more heavily. Conversely, a lower discount rate results in a higher present value for the annuity, because the future payments are discounted less heavily. Present value is an important concept for annuities because it allows individuals to compare the value of receiving a series of payments in the future to the value of receiving a lump-sum payment today.
Table of Contents
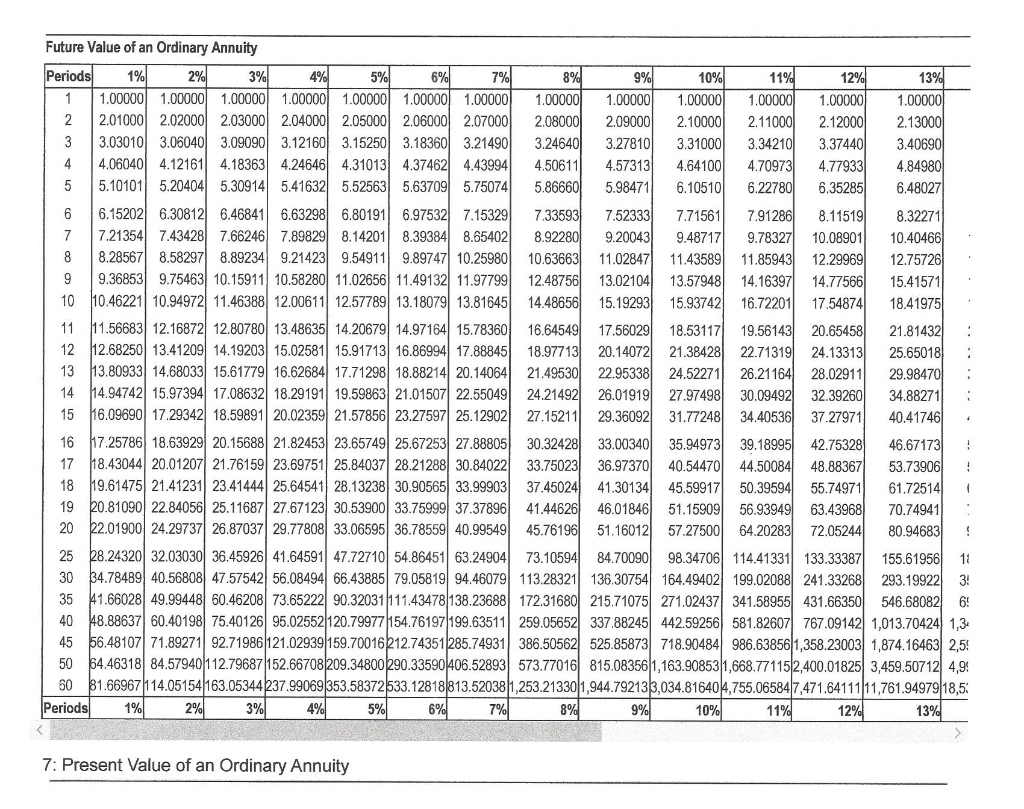
The present value of an annuity is the total value of all of future annuity payments. A key factor in determining the present value of an annuity is the discount rate. An annuity table, often referred to as a “present value table,” is a financial tool that simplifies the process of calculating the present value of an ordinary annuity. By finding the present value interest factor of an annuity (PVIFA) on the table, you can easily determine the current worth of your annuity payments.
How To Calculate The Value Of An Annuity
When the calculator is in annuity due mode, a tiny BGN appears in the upper right-hand corner of your calculator. When the calculator is in ordinary annuity mode there is nothing in the upper right-hand corner. The steps required to solve the future value of an annuity due are identical to those you use for an ordinary annuity except you use the formula for the future value of an annuity due.
- Annuity tables also provide a standard that can fairly value annuities of different amounts.
- But annuities can also be more of a general concept that describes anything that’s broken up into a series of payments.
- Are they received at the end of the contract period, as is typical with an ordinary annuity, or at the beginning?
Related Retirement Calculators:
If the contract defines the period in advance, we call it a certain or guaranteed annuity. A wide range of financial products all involve a series of payments that are equal and are made at fixed know the facts about the fair tax intervals. The two conditions that need to be met are constant payments and a fixed number of periods. For example, $500 to be paid at the end of each of the next five years is a 5-year annuity.
Present Value Formulas, Tables and Calculators
Except for minor differences due to rounding, answers to the exercises below will be the same whether they are computed using a financial calculator, computer software, PV tables, or formulas. For example, instead of paying $100 cash a person is allowed to pay $9 per month for 12 months. The interest rate is not stated, but the implicit rate can be determined by use of present value factors. This means that any interest earned is reinvested and will earn interest at the same rate as the principal. In other words, you earn “interest on interest.” The compounding of interest can be very significant when the interest rate and/or the number of years are sizable. The terms of your contract state that you will hold the annuity for seven years at a guaranteed effective interest rate of 3.25%.
Components of a Present Value Calculation
Because of the time value of money, money received today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future because it can be invested in the meantime. By the same logic, $5,000 received today is worth more than the same amount spread over five annual installments of $1,000 each. An annuity’s future value is also affected by the concept of “time value of money.” Due to inflation, the $500 you expect to receive in 10 years will have less buying power than that same $500 would have today.
The point where a particular interest rate (i) intersects a particular number of payments (n) is the annuity’s PVOA factor. When you multiply this factor by the annuity’s recurring payment amount, the result is the present value of the annuity. Using an annuity calculator or a financial spreadsheet set up for calculating the present value of an annuity is often more precise than using the preset annuity table. These tools are also helpful if your values fall outside the annuity table’s given ranges.
Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service. So the present value you’d need to invest today to cover five $1,000 payments, assuming a 5 percent interest rate, would be about $4,545.95. Therefore, the future value of your annuity due with $1,000 annual payments at a 5 percent interest rate for five years would be about $5,801.91.
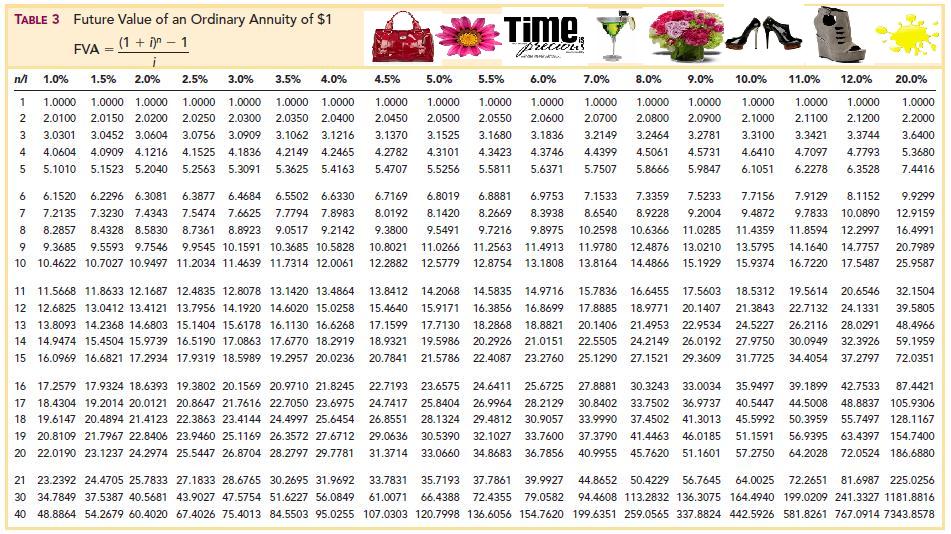
Similar to the future value, the present value calculation for an annuity due also considers the earlier receipt of payments compared to ordinary annuities. This reduces the present value needed to generate the same future income stream. This formula incorporates both the time value of money within the period and the additional interest earned due to earlier payments. This concept helps you compare future income streams with current investment opportunities, allowing you to make informed financial decisions. In simpler terms, it tells you how much money the annuity will be worth after all the payments are received and compounded with interest.
You buy an annuity either with a single payment or a series of payments, and you receive a lump-sum payout shortly after purchasing the annuity or a series of payouts over time. But annuities can also be more of a general concept that describes anything that’s broken up into a series of payments. For example, a lottery winner may opt to receive a series of payments over time instead of a single lump sum distribution. For a more exact way of determining the present value of an annuity, consider using an annuity calculator that you find online or an Excel or Google spreadsheet.
But even this simple example, which did not require an interest conversion, is cumbersome, and time-consuming, to solve using the formula. A financial calculator can quickly solve annuity problems, with the added bonus of not requiring an interest conversion in situations where the payment frequency and compounding frequency are not equal. If your annuity promises you a $50,000 lump sum payment in the future, then the present value would be that $50,000 minus the proposed rate of return on your money. An annuity is a contract between you and an insurance company that’s typically designed to provide retirement income.
Leave a Reply